When it comes to protecting our digital lives, Cyber Security professionals and Ethical Hackers play an important role in ensuring our safety. A Cyber Security expert is tasked with safeguarding computer systems from malicious attacks while an Ethical Hacker works to proactively identify weaknesses within the security system.
Both fields require a deep understanding of technology and keen knowledge of potential threats across various platforms.
Ethical hacking is an essential part of Cyber Security, and the two terms can be confusing for aspiring professionals and students. In this blog, we’ll explore the differences between Cyber Security and Ethical Hacking, highlighting how these seemingly disparate jobs can work together to create a safe online environment for all users.
Introducing Cyber Security – What is it and why is it important?
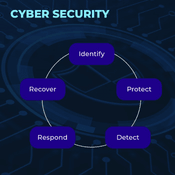
Cyber Security is the practice of securing computer systems, networks, application, and data from unauthorized access, theft, manipulation, disasters, and cyber-attacks.
The main objective of Cyber Security is to protect the sensitive data from security breaches, from malicious hackers or cyber criminals who exploit vulnerabilities in the system.
There are different types of Cyber Security which includes network security, application security, data security, disaster recovery, business continuity, identity management, cloud security, and many more.
Cyber Security is now essential for every individual, business, and government agency. With the increasing use of connected systems and devices, the potential for data breach or cyber-attacks has increased exponentially.
Given this, it is important to have adequate Cyber Security measures and protection in place to ensure that all our data remains safe from malicious entities.
What is Ethical Hacking?
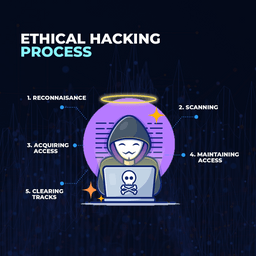
Ethical Hacking is commonly known as “White Hat Hacking” and Ethical Hackers are referred to as White Hat Hackers. It’s a practice of breaking into a system or network with the intention of identifying weaknesses and vulnerabilities in the network or system.
Ethical Hacking tests the security of the system and network and helps organizations to analyze their security and improvise them.
Ethical hackers search for vulnerabilities in the system or network using various methods like penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, social engineering, packet sniffing, among others.
The objective of a penetration tester is to find vulnerabilities and report it before bad actors/black hat hackers exploit them.
Articles you may like:
?Learn Ethical Hacking from Scratch: Know How?
?10 Best Ethical Hacking Books?
Cyber Security vs. Ethical Hacking: A Comparative Study
- Objective: A Cyber Security professional focuses on protecting computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, damage, or disruption. Ethical Hacking, on the other hand, involves intentionally penetrating systems with the goal of identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in order to improve their security.
- Legal Framework: Cyber Security experts operate within legal and ethical boundaries, ensuring compliance with laws and regulations. Ethical Hacking is also governed by legal frameworks, but it involves obtaining explicit permission from system owners to conduct security testing and vulnerability assessments.
- Intent: Cyber Security aims to prevent unauthorized access and defend against attacks by implementing security measures and protocols. Ethical Hacking, on the other hand, aims to identify vulnerabilities by simulating real-world attacks and adopting the perspective of malicious hackers.
- Knowledge and Skills: Cybersecurity experts require a broad understanding of security principles, risk management, compliance, and incident response. Ethical Hackers possess specialized skills in penetration testing, vulnerability assessment, exploit development, and reconnaissance techniques.
- Authorization: Cybersecurity professionals work within authorized frameworks to protect systems and data, often focusing on prevention and proactive measures. Ethical Hackers must obtain explicit authorization before conducting any testing or assessment activities on a target system.
- Scope: Cyber Security covers a wide range of activities, including network security, application security, data protection, security policies, and incident response. Ethical hacking specifically concentrates on identifying vulnerabilities, exploiting them, and providing recommendations for remediation.
- Perception: Cyber Security professionals are perceived as defenders of systems and data, working to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of information. Ethical Hackers are sometimes viewed with skepticism due to their association with hacking, but their purpose is to improve security through controlled and authorized testing.
- Approach: Cyber Security takes a proactive approach by implementing security controls, conducting risk assessments, and implementing incident response plans. Ethical Hacking adopts a more reactive and offensive approach, attempting to uncover vulnerabilities that may have been overlooked in the security design.
- Collaboration: Cyber Security professionals collaborate with various stakeholders, including system administrators, network engineers, developers, and management, to ensure comprehensive security. Ethical Hackers often work independently or in small teams, focusing on specific targets or objectives.
- Outcomes: The ultimate outcome of Cyber Security efforts is a secure and robust system with reduced risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. Ethical Hacking produces reports outlining vulnerabilities discovered, along with recommendations to address them, ultimately leading to improved security posture.
Understanding the Role of Ethical Hackers in Cyber Security
An Ethical Hacker is employed by organizations to act as an additional layer of defense and provide insight into potential threats before they can be exploited.
Security manager and analysts rely on Ethical Hackers to help them gain a better understanding of their environment and determine the best way to mitigate risks.
Ethical Hacking is critical for organizations looking to keep their systems secure from malicious actors, making it an essential part of any effective Cyber Security strategy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Cyber Security and Ethical Hacking are two interdependent components of an effective cyber security strategy. Cyber Security focuses on proactive measures to protect systems and data, while Ethical Hacking concentrates on actively identifying vulnerabilities and providing recommendations for remediation.
Both disciplines require a wide range of knowledge and skills as well as authorization from system owners before conducting any testing or assessment activities. Cyber Security professionals work with multiple stakeholders to ensure comprehensive security within authorized frameworks, while Ethical Hackers often work independently or in small teams to uncover potential threats.
Together, these two fields form the basis of a comprehensive approach to defending against malicious actors and protecting organizations from data breaches and unauthorized access.
The field of Cyber Security is often confused with yet two other major domains, that of Network Security and Information Security. If you wish to read on this topic, check out our blogs on:
?Cyber Security vs. Information Security?
?Cyber Security vs. Network Security?
We, at Syntax Technologies, can not only help you to develop expertise as a Cyber Security expert, but also assist you in preparing a strong foundation for a career in Ethical Hacking. Enroll today.