Cyber Crime is the Greatest Threat to Every Company in the World – Ginni Rometty (former CEO of IBM)
The increasing dependence on the technological sphere has had its own share of advantages and disadvantages. While these tech devices have become indispensable for the functioning of modern society; they have also become exceedingly vulnerable to Cyber attacks and threats.
While this is certainly not good news; on the flip side, it also means that Cyber Security as an important career option is here to stay. However, it is one thing to develop the skills of a Cyber Security expert and another to ace a Cyber Security Interview. The latter requires you to have a strong grasp over some of the most important Cyber Security Interview Questions.
?This blog will provide you with a list of top 40 Cyber Security Job Interview Questions, along with their answers, which will help you focus on the most relevant topics. The Cyber Security Questions mentioned in this blog, have been carefully curated in terms of looking at the domain from the diverse aspects of networking, operating systems, software and programming, Cyber attacks and so on.
?If you are someone who is looking to make his/her headway into the field of Cyber Security, do read our blog on ?How to Get into Cyber Security??
Cyber Security Questions: Basic Level
1. What are the different elements of Cyber Security?
The elements of Cyber Security refer to the different dimensions or types of Cyber Security. These are:
- Network security: It seeks to protect data which travels across devices in the network in order to make sure that it is not intercepted or changed.
- Information security: It provides protection to digital as well as physical data, safeguarding it against disruption, unauthorized access, destruction, disclosure and so on.
- Application Security: It refers to the process of evolving, testing and adding security features within applications in order to protect it from different kinds of Cyber Security threats.
- Operational Security: it refers to a specific dimension of risk management which prevent accessibility to sensitive and critical data, by cyber criminals, thereby ensuring data protection.
- Cloud Security: It refers to the entire collection of policies, technologies and services which ensures protection for cloud application, infrastructure and data from Cyber attacks. ?
- Disaster recovery and business continuity: The two ideas operate as a dyad wherein business continuity focuses on keeping the enterprise operational in the face of a cyber attack; while disaster recovery would deal with the steps taken by the enterprise to ensure restoration of data access.
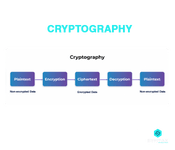
2. What is Cryptography?
This happens to be one of the most common Interview Questions for Cyber Security. Cryptography is essentially the practice of securing communication and information from being accessible to third parties who are referred to as adversaries.
These third parties are not the ones for whom the data is intended for and hence cryptography ensures that only the sender and the recipient of the message will be able to read it. It entails the conversion of data from a readable format to a non-readable format and vice-versa.
3. Differentiate between Threat, Risk and Vulnerabilities
On the face of it, the three terms might seem to have similar connotations. However, this happens to be one of the classic Cyber Security Technical Interview Questions and you as an aspiring candidate should be able to draw a line between the three.
- Threat: This refers to any form of potential harm or hazard which can steal or destroy data, cause problems for the organization?s assets or disrupt operations. A threat can be intentional or accidental and a threat actor can be an individual or group. Example: Data Breaches, Malware, Phishing and so on.
- Vulnerabilities: This is essentially a weakness or a flaw in the system (hardware, personnel, software) which can be exploited by a threat in order to attain its objectives. Example: Networking equipment exposed to the public is a form of physical vulnerability.
- Risk: It is the probability or the likelihood of a threat actor to exploit a vulnerability in order to harm a system. It is calculated by the given formula:
Risk = Threat Probability * Impact of Vulnerability
4. What is a firewall? What are its types?
A firewall operates as an obstacle between the Internet and a LAN (internal network and incoming traffic from external sources). It operates on the boundaries of a network, supervising network traffic and thereby blocking malicious traffic in the form of malware, viruses, worms and so on. It helps in managing inbound and outbound network traffic.
There are three common types of firewalls:
- ?Proxy Firewalls: Network traffic is filtered at the Application level?
- Packet-filtering Firewalls: Packets are analyzed and are permitted to pass through a firewall only when they match an established security rule-set?
- Stateful Multilayer Inspection (SMLI) Firewall: Packets are filtered at the Transport, Application and Network layers. Comparison is made with known trusted packets
The idea of a Firewall is often confused with that of Antivirus. To know more about the difference between the two; check out our blog on ?Difference between Firewall and Antivirus?
5. How can a firewall be set up?
The steps are:
- ?Username/Password: The default password of a firewall device should be altered?
- Remote Administration: This feature should be disabled?
- Port Forward: Appropriate ports should be configured in order to ensure seamless execution of certain applications?
- DHCP Server: The DHCP Server should be disabled when the firewall is being installed in order to avoid any conflict?
- Logging: Logging should be enabled and it is important to understand how to view logs in order to troubleshoot potential attacks and firewall issues?
- Policies: Robust security policies should be configured with the firewall
6. What is a traceroute?
Traceroute works as a network diagnostic tool which helps in identifying the path taken by a packet. By way of listing all the points which a packet passes through, a traceroute helps in tracking the route that a packet takes when it is sent across an IP network.
Thus, it shows the IP addresses of all the routers which it pinged in its journey between the source and the destination. Traceroute helps in identifying the points of failure and the point at which connection breaks or stops.
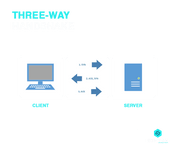
7. What is a three-way handshake?
It is one of the methods used within a TCP/IP network when a connection is sought to be made between a local host and the server. It is referred to as a three-way handshake because it is essentially a three-step process for the negotiation of acknowledgement and synchronization of packets between the client and the server before the communication begins.
The three steps:
- The connection is made when the server receives the SYN (Synchronize) Packet from the client
- The server responds to the request by the client by sending the SYN+ACK Packet
- The response of the server is in turn acknowledged by the client with the ACK (Acknowledgement) Packet
8. Explain the difference between Hashing and Encryption
Hashing helps in transforming data into a smaller fixed value which is referred to as the key and which represents the original data. Encryption, on the other hand, is the strategy of encoding data in a way that only the authorized user with the password or the key will be able to access the original data.
The hash key or the code cannot be reverted to the original information. It can be mapped and compared with another hash code, but it cannot be used to get the original data. Encrypted data can be converted back to original data through the process of decryption.
The objective of hashing is to retrieve and index data from a database. It helps in data verification. The objective of encryption is to transform data into forms which keeps it hidden. Thus, it helps in secured transmission of data.
9. Differentiate between Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing
Vulnerability Assessment is the process of identifying, defining and prioritizing flaws in computer networks, systems, applications and infrastructure. By way of telling how susceptible a network is to a potential attack, VA helps in providing the necessary information to the organization for rectifying the vulnerabilities.
Penetration Testing is also known as pen-testing or ethical hacking. In this case, the organization would have already taken all possible steps for preventing the system from being hacked. However, in order to be doubly assured, they try to intentionally find vulnerabilities which could potentially be hacked and thus prevent attackers from exploiting them.
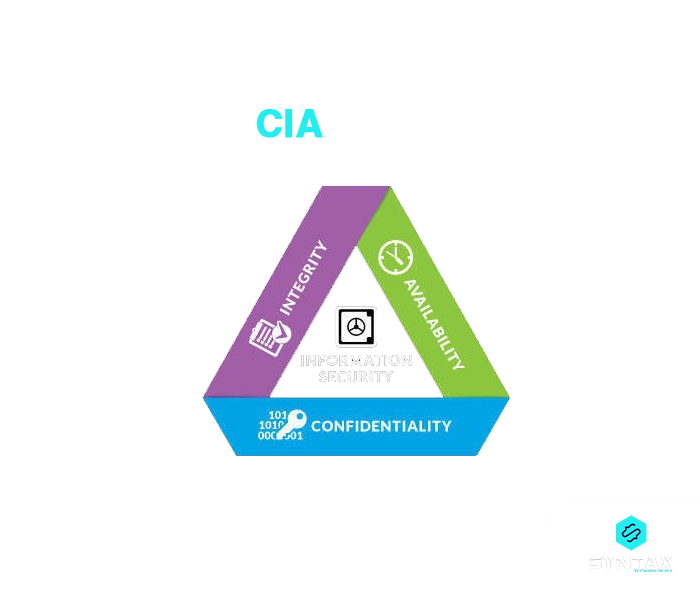
10. What is the CIA Triad?
It is essentially a security model which forms the basis of Information Security. It includes the three notions of Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability.
- Confidentiality: Prevention of unauthorized access to sensitive information
- Integrity: Protection of modification or deletion of data by unintended person?
- Availability: Ensure the availability of data as and when needed
11. What is a Response Code?
Whenever a request is made by a client to the server, the server responds with HTTP response codes. These codes are indicative of whether the HTTP response has been completed or not.
- 1xx: Informational: The request is received and the process continues.
- 2xx: Success: The action is received, understood and accepted successfully.
- 3xx: Redirection: In order to complete the action, it is necessary to take further action.
- 4xx: Client Error: The request is not fulfilled or has incorrect syntax. ?
- 5xx: Server Error: The server fails to complete a valid request.
12. What is DNS and VPN?
DNS is the abbreviated version of Domain Name System. It helps in mapping the domain name into its corresponding IP address.
One of the most common Cyber Security Questions, VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. It helps in creating an encrypted and safe connection by providing online privacy and anonymity from a public internet connection. Thus, for you as a user, VPN can safeguard your online activities like online shopping, paying bills and so on. VPN operates on the foundation of encrypted data transfer.
13. What are the common forms of Cyber Attacks?
This happens to be one of the classic Cyber Security Interview Questions. Some of the common forms of Cyber attacks are:
- Phishing: Users are sent messages, links and email disguised from sources which the victims have reason to trust. Users are duped into clicking these links which grants access to information to the hackers.
- SQL Injection: The hacker might send a query which gains entry into the database of the user?s webpage through the SQL injection.
- Ransomware: Users are denied access to their own files and access to data is sought to be made available through the payment of a specific amount demanded as ransom. ?
- Man-In-The-Middle Attack: It occurs when criminals position themselves between the server and client and are able to indulge in malicious activities by secretly being a part of a critical conversation.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DOS): It occurs when a system or network is overwhelmed by unwanted traffic, resulting in the inability to respond to requests.?
- Cross-site Scripting (XSS): A cybercriminal might send a suspicious code to an otherwise normal website. If the website allows the code to get attached to its own, it bundles the two scripts before it is send to the user. When the script executes, the hacker would receive a cookie which might help in collecting critical information.
14. What is port scanning?
Port Scanning is a strategy for identifying ports which are closed or open on a network. Both hackers as well as administrators use port scanning. The former use it in order to detect the weak points which could be exploited for getting into a system. The latter use it in order to test the strength of firewall and network security.
Some of the common port scanning techniques are:
- Ping Scan
- Stealth Scanning
- UDP
- TCP Connect
- TCP Half-Open
15. What is Data Leakage?
Data leakage implies the intentional or unintentional transmission of data from an internal source to an external destination which is unauthorized. It usually entails the disclosure of confidential information and the mode of transmission can be physical, electronic, email, web, storage devices and so on.
Data Leakage types:
- Accidental Data Leakage: Data is sent to an unauthorized entity accidentally and unintentionally
- Intentional Leakage/Malicious Insiders: An unauthorized entity receives data from an internal authorized entity who sends it intentionally?
- Hacking of the System: When the system is hacked by hackers, it might result in data breach
?
Cyber Security Interview Questions: Intermediate Level
16. Differentiate between Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption
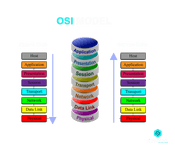
17. What is the OSI model?
OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection model. This model was introduced by the International Organization for Standardization in order to lay down guidelines or provide a reference model for the way in which applications should interact with each other over a network. It serves as a reference for developers and vendors for facilitating the interoperation of software programs and communication products.
The different layers of the OSI model are:
- Physical Layer: As the lowest level of the model, this layer facilitates the conversion of data into electrical impulses and its transmission across a physical medium.
- Data Link Layer: This layer provides for the encoding and decoding of data packets. Apart from overlooking the node to node delivery of message, the layer determines the format of data in the network
- Network Layer: This layer provides for logical addressing and routing. Thus, it specifies the path which the data will take
- Transport Layer: This layer provides for end-to-end connections and facilitates the transmission of data using TCP/UDP protocols
- Session Layer: This layer controls ports and sessions in order to ensure the maintenance of connection between the sender and the receiver
- Presentation Layer: This layer provides for the formatting and encryption of data. It translates data into the application layer format
- Application Layer: This is the layer at which the user interacts with the application and services are provided to the end-user. Thus, it deals with all sorts of data that a machine generates
18. Explain the difference between IDS and IPS
IDS stands for Intrusion Detection System. As the name suggests, Intrusion Detection Systems refers to a network infrastructure which can be used for detecting and identifying intrusion by hackers. It helps in detecting malware and other forms of violations.
IPS stands for Intrusion Prevention System. It refers to a network infrastructure for the detection as well as prevention of intrusions by hackers. It does not deliver malicious packets if the traffic is from known threats in databases.
19. What is Identity Theft? How to prevent it?
Identity theft essentially refers to a criminal activity when one person uses the personal identifying information like name, credit card number and others, of another person, for committing fraud like unauthorized purchases and transactions.
Identity Theft can be prevented through the following steps:
- Personal records should be protected and one should avoid sharing any kind of confidential information
- Unique and strong passwords should be used, which should also be changed at regular intervals
- Social Security Number should be protected
- Software and systems should be regularly updated; latest version of browser should be used
- Robust security solutions should be used to protect financial data
- Banking information should never be shared over untrustworthy websites
20. Who are the different types of hackers?
Black Hat Hackers: These are individuals who acquire illegal and unauthorized access to a system and use their skills for breaching confidential information. Their objective is generally to steal critical data, disrupt the operation of the system, block network connection or perform other kinds of malicious activities like injecting viruses, malware and so on.
White Hat Hackers: These are Ethical Hackers who perform the task of Penetration Testing and Vulnerability Assessment. They do break into a system, but they do so by remaining within the legal boundaries of rules set by the organization. They act as security specialists whose role is to identify vulnerabilities and flaws in the existing system which can potentially be misused.
Grey Hat Hackers: These individuals share the traits of a black and a white hat hacker. Like a white hat hacker, the intention of a grey hat hacker for hacking a system is not necessarily bad; and like a black hat hacker, a grey hat hacker also does not have permission to break into the system. However, unlike a black hat hacker, they do not exploit the vulnerabilities and generally report the same to the owner in lieu of small rewards.
21. What is SSL Encryption?
It stands for Secure Sockets Layer which is an industry-standard security protocol, helping to create encrypted connections between the Browser and the Web Server. It helps in maintaining data privacy in order to protect user information in online transactions. It helps in guaranteeing data integrity, security and authentication.
22. How can you reset a password protected BIOS Configuration?
As a pre-boot hardware system, BIOS has its own storage mechanism for preferences and setting, and when set up with a password, it can lock the operating system. The BIOS password can be reset through some techniques, like:
- Unplugging the PC and removing the CMOS battery for 15-20 mins
- Third party software such as Kiosk and CmosPwd can be used
- Making use of MS-DOS
- Utilizing a motherboard jumper
23. What is brute force attack?
It can be regarded as a trial and error method wherein a hacker tries all possible permutations and combinations in order to guess the target password as they try to break in. These attacks are automated where the software/tool automatically tries to login with a list of credentials. Some of the ways to prevent a brute force attack can be:
- Lengthy passwords are often difficult to crack
- It is generally advisable that passwords should be complex. It can include different combination of characters, along with upper and lower case letters
- Limits should be set to login failures. If the attempt crosses the limit then an OTP or email can be sent which can be used to login the next time
24. What is the XSS Attack? How can it be prevented?
Cyber Security Questions on the specific types of Cyber Attacks are among the favorites of interviewers.
Cross-site scripting or XSS is a form of Cyber Attack wherein a cybercriminal might send a suspicious code to an otherwise normal website. If the website allows the code to get attached to its own, it bundles the two scripts before it is sent to the user. When the script executes, the hacker would receive a cookie which might help in collecting critical information.
Some of the ways to prevent a XSS attack are:
- Authenticate the inputs of the user
- Anti-XSS tools can be employed
- Resort to encoding
- XSS HTML Filter can be used
- Software should be regularly updated
25. What are honeypots?
Honeypots are decoy computer systems or attack targets which are intentionally set up in order to understand how attackers exploit vulnerabilities. It records all interaction, action and transaction with the users. Honeypots are generally of two kinds:
- Production honeypot: It captures real information for the administrators in order to help them to access vulnerabilities?
- Research honeypot: It is employed by educational organizations and institutions for researching upon the tactics and motives of the black hat community
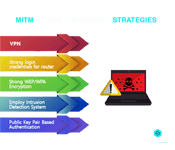
26. Explain the MITM attack
This is considered to be quite a sneaky form of Cyber Attack. In this case, the hacker or the cyber criminal eavesdrops by placing himself in the middle of a communication between two parties. If the communication is taking place between party X and party Y; then the hacker joins the communication and impersonates as X to party Y and as Y to party X. In doing so, both the parties are duped into transmitting the data to the hacker as they wrongly believe that they are doing so to the other party. The objective of a MITM attack is often to alter and steal information.
27. Explain the DDOS attack
DDOS stands for Distributed denial-of-service. This Cyber attack is meant to subject the system or the website to huge unmanageable traffic, over and above the capacity of the server. The ultimate objective is to make the system inaccessible to its genuine users/clients. There are two types of DDOS attacks:
- Flooding Attacks
This results when the system is subjected to massive amounts of traffic which it cannot handle. This is executed through continuous sending of packets by the attacker through automated software.
- Crash Attacks
In this case the hacker exploits vulnerability in the targeted website to result in a system crash. This results in denial of services to the legitimate users.
28. What is Phishing?
This happens to be one of the classic Cyber Security Interview Questions. Phishing happens to be a deceptive Cyber Attack wherein the attacker puts up a fake appearance as a trusted entity (legitimate company/person) in order to extract sensitive information from random individuals by manipulating them. Phishing is made successful through different forms of user interaction. This can be through instant messages or calls for acquiring confidential data such as credit card information, emails containing malicious links resulting in download of risky attachments and so on.
Articles you may like:
?Difference between Phishing and Pharming?
?Spoofing vs. Phishing: A Comparative Study?

29. What is Two-Factor Authentication?
Two-Factor Authentication or 2FA is a security process to confirm the identity of a person who happens to be accessing an online account. It results in adding an extra layer of verification and scrutiny. In order to access the account, in addition to the password, users are generally required to enter a unique identification code which is sent to them via emails or text messages. The password along with the matching security code grants access; otherwise the user is blocked from entering the website.
Cyber Security Job Interview Questions: Advanced Level
30. What are salted hashes?
There can be a situation when two users happen to have the same password which results in the creation of identical password hashes. One of the main disadvantages of such an eventuality is that an attacker can crack such a password with ease through a brute-force or dictionary attack.
In order to avoid this, a salted hash is implemented. Salted hashes help in randomizing hashes by appending or prepending a salt (random string) to the password before hashing. This results in the creation of two entirely different hashes and which can then be used to protect the password.
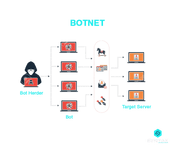
31. What is a botnet?
Botnet is often referred to as the robot network. It is a kind of malware which infects an array of computers and brings them under the control of a single hacker who then becomes the ?bot herder?. A single computer system becomes the bot which comes under the control of bot herders. Since a number of computer systems are made to operate under a single attacker, they are able to use every bot to perform coordinated and simultaneous criminal actions.
32. Differentiate between VPN and VLAN
33. What is SQL Injection?
Database servers run behind web applications. When an attacker executes malicious commands in the server, it takes the form of an injection attack and is referred to as SQL injection. The objective of this Cyber Attack is to acquire illegal access to confidential data and information like intellectual property details, client data, personal information and so on.
In addition to this, under this kind of attack, the cybercriminal is also able modify, delete or add records in the database, thereby resulting in data integrity loss for an organization.
34. Explain the difference between Stream Cipher and Block Cipher
This is also one of significant Cyber Security Technical Interview Questions.
35. What is network sniffing?
Network Sniffing is a strategy/tool used for analyzing or evaluating packets of data sent over a network. A specialized hardware or a software program is used for the purpose. It can have a number of objectives:
- It can be used for capturing confidential data, such as password
- It can be used for eavesdropping on chat messages
- Can be used for monitoring data package over a network
36. Differentiate between virus and worm
A virus operates as a malicious executable code which is made to be attached to another executable file. It can result in deletion or modification of data. It requires a host program to be executed and is linked with .xls, .com, .doc, .exe and so on.
Unlike a virus, a worm does not alter a program. It multiplies by generating its own copy and spreading through the client?s email. It results in slowing down the computer. Can be manipulated with remote control and does not require any host to function. Its goal is to consume the resources of the system and can be linked with any file on a network.
37. What is an ARP?
This is another of the classic Cyber Security Interview Questions. ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol. It is a communication protocol under the network layer in the OSI model. Its objective is to find the MAC address for a specific IP address in the system. It helps in converting the 32-bit IPv4 address into a 48-bit MAC address.
The operation of ARP:
- Frames are broadcasted to the entire network through an ARP request
- The ARP request is received by all the nodes on the network
- The request is sought to be matched with the ARP table in order to find the specific MAC address
- If there is no match, the packet is discarded by the nodes
- If there is a match, an ARP response is sent back by the target to the original sender
38. What are social engineering attacks?
Social Engineering attacks are forms of Cyber Attacks wherein people are manipulated into disclosing their confidential and sensitive data and information. They are essentially of three types:
- Phishing Attack
- Spear Phishing Attack
- Whaling Phishing Attack
39. What are the different protocols which fall under the TCP/IP Internet layer?
40. What is Cognitive Cyber Security?
Cognitive Cyber Security entails the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology which is premised on human thought mechanism, for detecting potential threats to the digital and physical systems. The idea is to impact human knowledge to a self-learning system. It makes use of pattern recognition, natural language processing and data mining for identifying threats, forecasting its effects and developing reactive strategies.
Conclusion
The field of Cyber Security is definitely an exhaustive one, with infinite opportunities. Having a good grasp over some of the most important areas within the domain can provide you with a good starting point as you prepare for a Cyber Security interview.
With the same objective in mind, this blog seeks to provide you with a fair idea of some of the classic and significant Cyber Security Interview Questions along with their answers. The list of Cyber Security Questions has been attentively prepared in order to help you brush up your knowledge and understanding of the field.
We, at Syntax Technologies, provide you with an unparalleled opportunity for being a part of a program which not only helps you in developing skills in line with the demands of a Cyber Security expert, but guarantees end to end assistance with complete mentorship. So if you wish to set your foot on this lucrative path, begin your journey with us. Enrol now for our Cyber Security Course.